Are You Suffering from Acne? Come Here and Gets Solutions..
Introduction of Acne: Acne is the most common skin condition, which
occurs when your hair follicles become plugged with oil and dead skin cells. Propionibacterium
acnes (P. acnes) is the name of the bacteria that live on the skin and
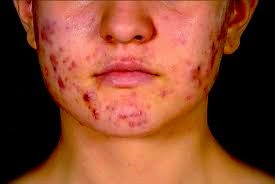
contributes to the infection of pimples. It usually appears on the face,
forehead, chest, upper back and shoulders. Acne is most common among teenagers,
though it affects people of all ages. Acne is a chronic, inflammatory skin
disease that results in whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, cysts, and nodules. It
is not dangerous, but it can leave skin scars.
They tend to look on the face, back, chest,
shoulders, and neck. Skin cells, sebum, and hair can clump gather into a plug. This plug gets
infected with Bacteria and swelling results. A pimple starts to develop when
the plug begins to break down. The Experiment suggests that the severity and
frequency of acne depend on the strain of bacteria. One strain helps to keep
the skin pimple-free.
Risk factors for Acne:
Age. People of all ages
can get acne, but it's most common in teenagers. (It affects 3 in every 4
people aged 11 to 30 years)
Hormonal changes. Such changes are usually common in
teenagers, women, and girls, and people using certain medications, including
those caused containing corticosteroids, androgens or lithium.
Family history. Genetics plays a
role in acne. If both parents had acne, you're likely to develop it, too.
Greasy or oily substances. You may create acne where your skin comes
into contact with oily lotions and creams or with grease in an action area,
such as a kitchen with fry vats.
Friction or pressure on your skin. This can be caused by items such as
telephones, cell phones, helmets, tight collars, and backpacks.
Stress: Stress
doesn't cause acne, but if you have acne already, it may make it worse.
Other causes include: Greasy cosmetics,
Emotional stress, Menstruation.
Human skin has pores
that connect to oil glands under the skin. Follicles connect the glands to the
pores. Follicles are small sacs that produce and secrete the liquid. The glands
produce an oily liquid called sebum. Sebum carries dead skin cells via the
follicles to the surface of the skin. A small hair grows through the follicles
out of the skin. Pimples grow when these follicles get blocked, and oil builds
up under the skin.
Acne develops when
sebum — an oily substance that lubricates your hair and skin — and dead skin
cells plug hair follicles. Bacteria can trigger inflammation and infection
resulting in more severe acne.
Types of Acne:
Acne pimples various
in size, color, and level of pain. The following types are possible:
Blackheads: Clearly visible, they are black and
appear on the surface of the skin.
Papules: Small, usually pink
bumps, these are visible on the surface of the skin.
Pustules: Clearly visible on
the surface of the skin. They are red at their base and have pus at the top.
Nodules: Clearly visible on
the surface of the skin. They are large, solid, painful pimples that are
embedded deep in the skin.
Cysts: Clearly
visible on the surface of the skin. They are painful and filled with pus. Cysts
can cause scars.
Treatment of Acne:
Treatment depends on age, severity, types and
persistent the acne.
Topical medications: The topical medications for acne are as
follows:
Retinoid and
retinoid-like drugs. These come as creams, gels, and lotions.
Retinoid drugs are derived from vitamin A (Avita, Retin-A, others), adapalene
(Differin) and tazarotene (Tazorac, Avage)
Antibiotics. These
work by killing excess skin bacteria and reducing redness. For the first few
months of treatment, you may use both a retinoid and an antibiotic. (Benzaclin,
Duac, Acanya) and erythromycin with benzoyl peroxide (Benzamycin). Topical
antibiotics alone aren't recommended.
Dapsone. Dapsone
(Aczone) 5 percent gel twice daily is recommended for inflammatory acne,
especially in adult females with acne. Side effects include redness and
dryness.
Benzoyl peroxide: kills
bacteria, accelerates the replacement of skin, and slows the production of
sebum
Salicylic acid: assists
the breakdown of blackheads and whiteheads and helps reduce information and
swelling
Azelaic acid: strengthens
cells that line the follicles, stops sebum eruptions, and There is cream for
acne reduces bacterial growth. But other forms are used for rosacea.
Oral medications:
Antibiotics. For moderate to severe acne,
you may need oral antibiotics to reduce bacteria and fight inflammation.
Usually the first choice for treating acne is tetracycline — such as
minocycline or doxycycline — or a macrolide.
Combined oral
contraceptives. Four combined
oral contraceptives are approved by the FDA for acne therapy in women who also
wish to use them for contraception.
Anti-androgen agents. The drug spironolactone (Aldactone) may be considered for
women and adolescent girls if oral antibiotics aren't helping. It works by
blocking the effect of androgen hormones on the sebaceous glands. Possible side
effects include breast tenderness and painful periods.
Isotretinoin. Isotretinoin (Amnesteem,
Claravis, Sotret) is a powerful drug for people whose severe acne doesn't
respond to other treatments.
Some Tips for Managing Acne:
Here are some tips for managing acne are following,
Ø
Wash your face no more than twice each day with warm water and
mild soap made especially for acne.
Ø
Reduce Swelling pimples,
gently apply ice for a minute.
Ø
Wash hands frequently, especially before applying lotions,
creams, or makeup.
Ø
For large acne cysts try Corticosteroid
Injections
Ø
Try Tea Tree Oil for massage face.
Ø
Clean spectacles regularly as they collect sebum and skin
residue.
Ø
Choose makeup for sensitive skin and avoid oil-based products.
Remove makeup before sleeping.
Ø Avoid anxiety and stress, as it can
increase production of cortisol and adrenaline, which exacerbate acne.
Ø
Avoid excessive sun
exposure, as it can cause the skin to produce more sebum. Several acne
medications increase the risk of sunburn.







Comments
Post a Comment